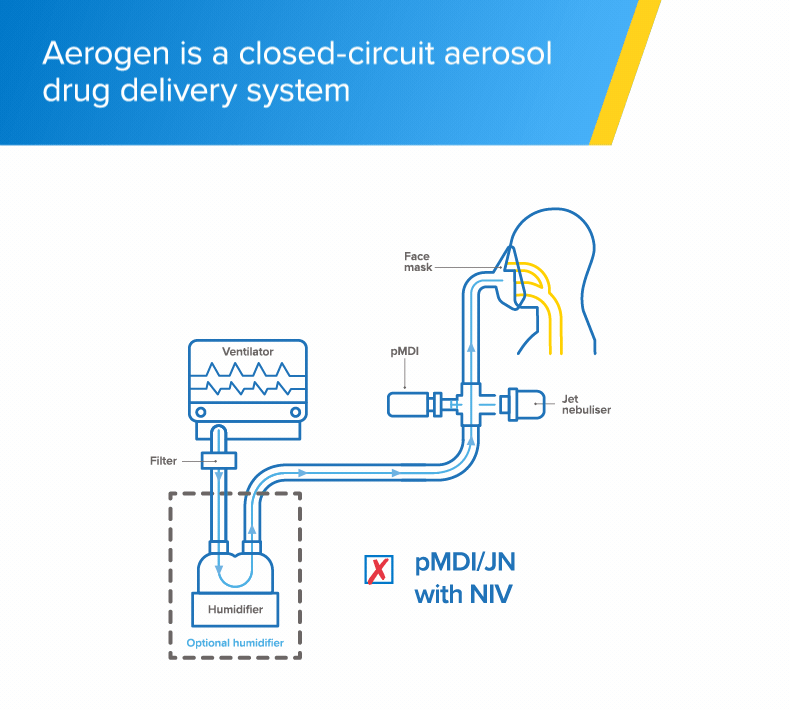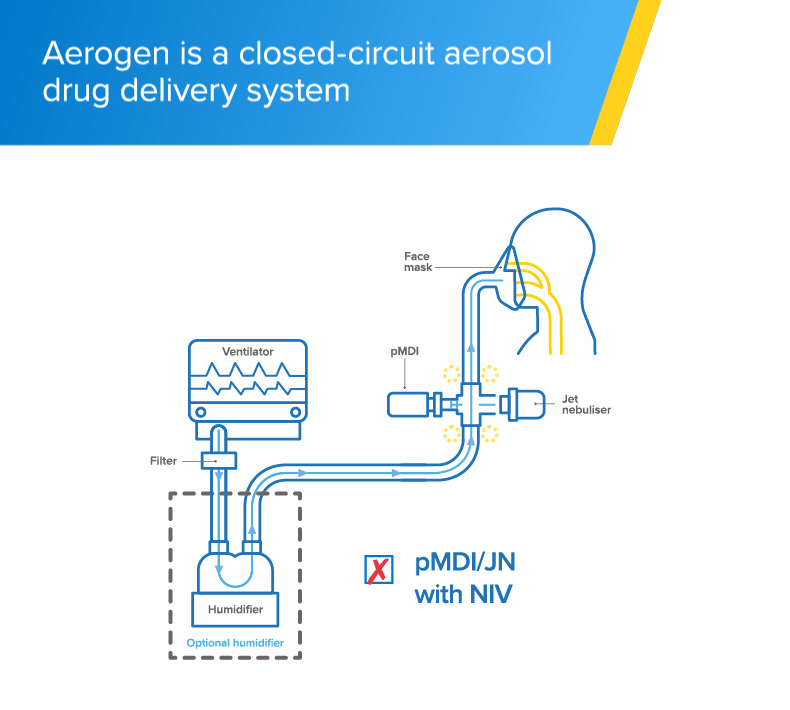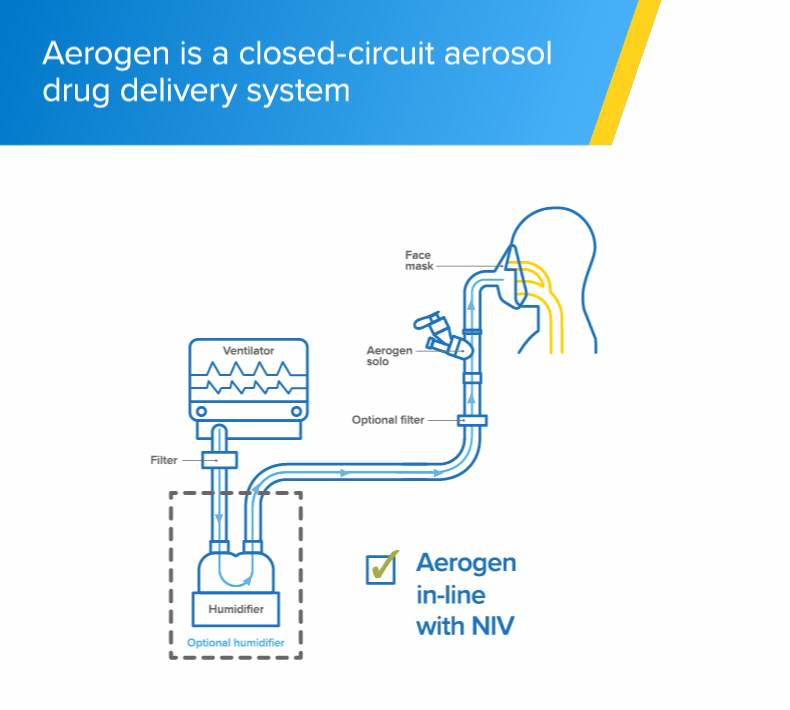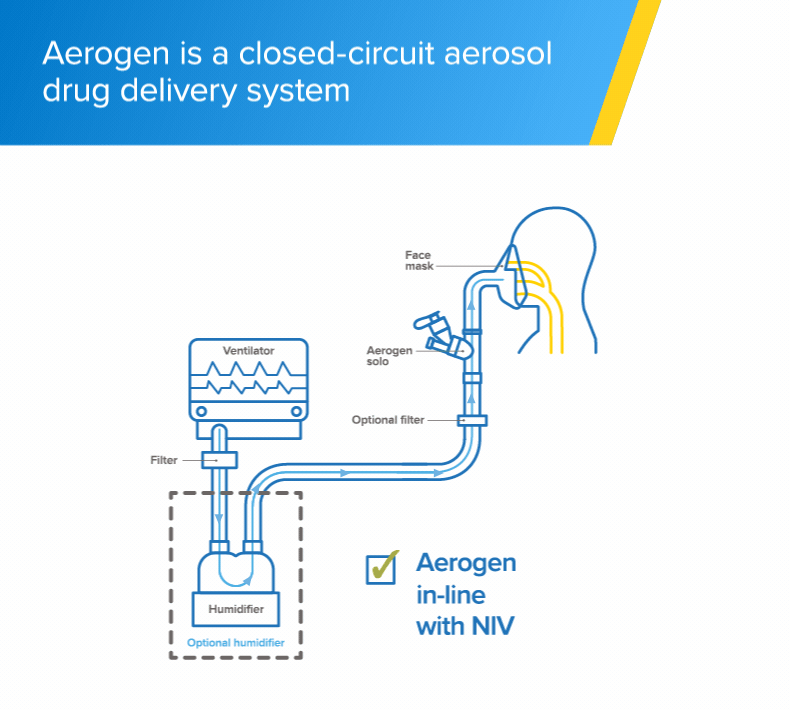
Non-invasive ventilation
The Aerogen Solo vibrating mesh nebuliser delivers aerosol medication to your patients during non-invasive ventilation (NIV)1
Patient care
The Aerogen Solo vibrating mesh nebuliser optimises aerosol drug delivery†2,‡3
- The Aerogen Solo – a vibrating mesh nebuliser – can rotate within the T-piece allowing various patient positions1
- Virtually silent drug delivery,1 keeping a calm environment for your patients
†Study performed in healthy subjects compared to a jet nebuliser
‡Study performed in stable subjects with moderate-to-severe COPD compared to a jet nebuliser
Ease of use
The Aerogen Solo vibrating mesh nebuliser simplifies the workflow
- The Aerogen Solo vibrating mesh nebuliser fits in-line with no added flow and no interruption of therapy during the administration of medication1
- One system throughout a patient's respiratory journey (IMV, NIV, HF, SV),1 supporting continuity of care
†Please refer to 30-354 REV U Aerogen Solo Instruction Manual when using Aerogen
†Using Aerogen
![]()
Effectiveness
Aerogen Solo facilitates effective medication delivery during non-invasive ventilation2-4
In studies, aerosol drug delivery with Aerogen via non-invasive ventilation was associated with:
- ~4x more medication delivered to the lungs compared to jet nebulisers†2,‡3
- Significantly less medication left in the cup compared to jet nebulisers‡3
†Study performed in healthy subjects
‡Study performed in stable subjects with moderate-to-severe COPD

Aerosol delivery via BiPAP
Representative scintigraphic images during nebulisation with non-invasive ventilation using a jet nebuliser (A) and Aerogen (B) in healthy adults.2
Guidelines
Clinical and scientific societies around the world recommend the use of closed-circuit nebulisers for the management of patients with COVID-19 requiring aerosol drug delivery:
- GOLD: Science Committee Report 20235
- AARC: Guidance 20206
- ISAM: Interim Guidance 20207
- Spanish Scientific Societies: Expert Clinical Consensus 20208
- Chinese Thoracic Society: Respiratory Care Committee 20209
- Indian Society of Critical Care Medicine: Position Statement 202010
- Indian Chest Society: Guidance 202011
Globally renowned
Aerogen technology has been in use for over 25 years, in more than 80 countries globally and is associated with over 300 clinical papers and publications.12 Aerogen is the partner of choice for the world's leading ventilator companies for aerosol drug delivery.12






Enquiries
The Aerogen team and our representatives are available globally to answer your questions, provide an online demonstration and place orders
- 30-354
REV U Aerogen
Solo Instruction Manual.
- Galindo-Filho VC, Ramos ME, Rattes CS, et al. Respir Care. 2015;60(9):1238-1246.
- Galindo-Filho VC, Alcoforado L, Rattes C, et al. Respir Med. 2019;153:60-67.
- AlQuaimi MM, Fink JB, Ari A. J Respir Dis Lung Dis. 2017;2:1018.
- Global Initiative for the Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease: 2023 report. Available at: https://goldcopd.org/2023-gold-report-2/ (accessed 06 December 2022).
- American Association for Respiratory Care SARS CoV-2 Guidance Document. https://www.aarc.org/wp-content/
- Fink JB, Ehrmann S, Li J, et al. J Aerosol Med Pulm Drug Deliv. 2020;33(6):300-304.
- Cinesi Gómez C, Peñuelas Rodríguez Ó, Luján Torné M, et al. Med Intensiva (Engl Ed). 2020;44(7):429-438.
- Respiratory care committee of Chinese Thoracic Society. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2020;17(0):E020.
- Kumar S, Mehta S, Sarangdhar N, et al. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2021;15(4):519-535.
- Swarnakar R, Gupta NM, Halder I, et al. Lung India. 2021;38(Supplement):S86-S91.
- Aerogen Data on File.
GL-3461-1-EN












